Introduction
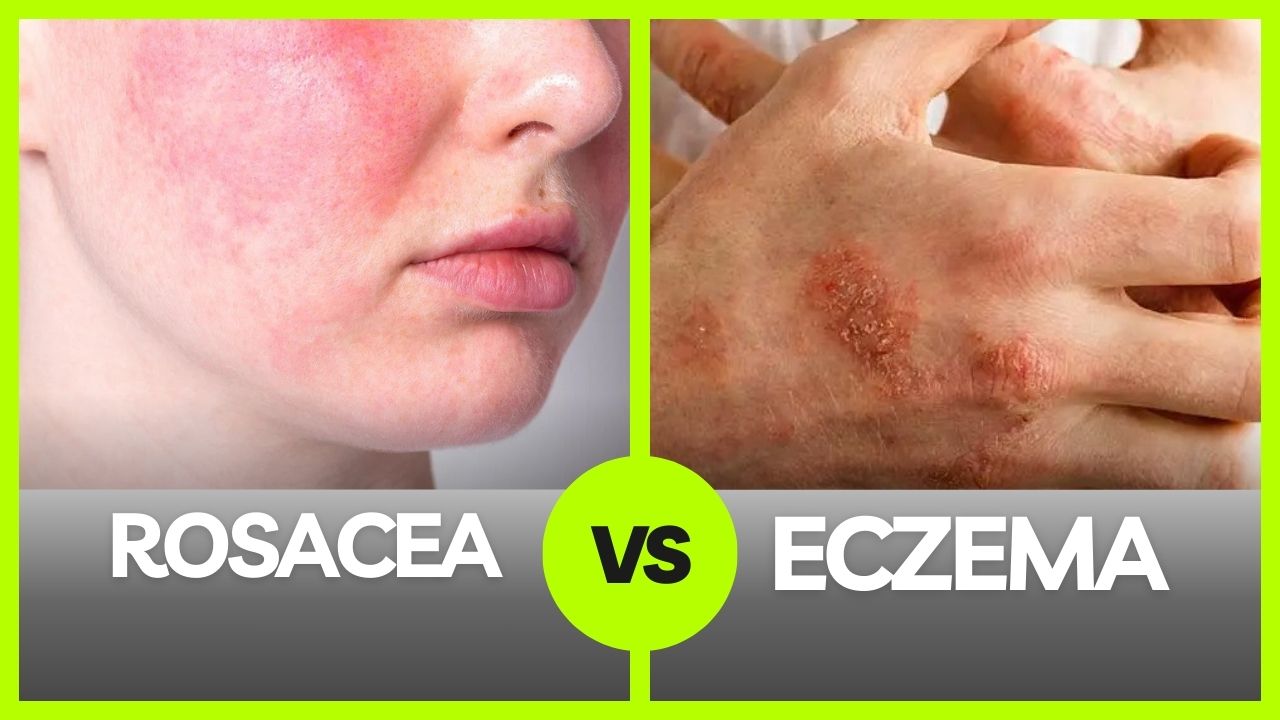
Have you ever wondered why some people have red, irritated skin that just doesn’t seem to go away? You’re not alone. Conditions like eczema and rosacea affect millions of people worldwide, leading to discomfort, self-consciousness, and a constant search for solutions. While both involve redness and inflammation, they’re distinct in causes, symptoms, and treatments. Let’s dive deep into what makes eczema and rosacea different, how to identify them, and ways to manage these conditions for healthier skin.
What is Eczema?
Definition and Overview
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a common skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While eczema often starts in childhood, it can affect people of all ages, often flaring up periodically and then subsiding.
Types of Eczema
Eczema isn’t a one-size-fits-all diagnosis; it comes in different forms:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common type, linked to genetics and allergies.
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by contact with irritating substances, like certain soaps or fabrics.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Small, itchy blisters usually on the hands and feet.
- Other types, such as nummular and seborrheic dermatitis, add to the variety of eczema’s manifestations.
What is Rosacea?
Definition and Overview
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes, small bumps that resemble acne. It tends to appear in adults, particularly those with fair skin, and can worsen over time without treatment.
Types of Rosacea
Rosacea can manifest in various forms, with each type requiring specific care:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea: Characterized by flushing and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Often mistaken for acne due to its red bumps.
- Phymatous Rosacea: Causes thickening of the skin, especially on the nose.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affects the eyes, causing redness and irritation.
Causes of Eczema
Understanding eczema’s causes can help in managing and preventing flare-ups:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies increases the likelihood.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to allergens, pollutants, and even cold weather can trigger eczema.
- Immune System Response: Eczema is often linked to an overactive immune response, leading to inflammation.
Causes of Rosacea
While the precise cause of rosacea remains unclear, certain factors increase susceptibility:
- Genetics: Like eczema, rosacea often runs in families.
- Environmental Triggers: Sun exposure, stress, and hot weather can provoke flare-ups.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Factors: Spicy foods, alcohol, and hot drinks are common culprits in triggering rosacea symptoms.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms vary in intensity but often include:
- Itching and Redness: The hallmark of eczema, itching can range from mild to severe.
- Dry Patches: Areas of skin can become rough, dry, and flaky.
- Swelling and Cracking: In more severe cases, skin can crack, bleed, or become swollen.
Symptoms of Rosacea
The symptoms of rosacea are more focused on the facial area and include:
- Persistent Redness: Often resembling a blush or sunburn that doesn’t fade.
- Visible Blood Vessels: Blood vessels may become more visible, particularly on the cheeks and nose.
- Bumps and Pustules: Red bumps that can be mistaken for acne.
Key Differences Between Eczema and Rosacea
Though eczema and rosacea share some similarities, they differ significantly:
Affected Areas of the Skin
- Eczema: Can appear almost anywhere, but commonly affects hands, feet, and areas prone to friction.
- Rosacea: Primarily affects the face, particularly the cheeks, nose, and forehead.
Appearance of Symptoms
- Eczema: Dry, flaky patches that can crack or ooze.
- Rosacea: Persistent redness, often with visible blood vessels and bumps.
Age of Onset
- Eczema: Often starts in childhood.
- Rosacea: Typically begins in adulthood.
Diagnosis of Eczema and Rosacea
Proper diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Dermatologists diagnose these conditions through physical examinations and may perform skin tests or allergy testing to identify triggers.
Treatment Options for Eczema
Eczema treatments focus on soothing inflammation and preventing flare-ups:
Topical Treatments
Steroid creams and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory creams can help control flare-ups.
Oral Medications
For severe cases, doctors may prescribe oral medications to reduce inflammation.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Using gentle, fragrance-free cream and avoiding known triggers is crucial for eczema management.
Treatment Options for Rosacea
Rosacea treatments aim to reduce redness and prevent flare-ups:
Topical Treatments
Creams with ingredients like metronidazole and azelaic acid are commonly prescribed.
Oral Medications
Antibiotics and, in some cases, isotretinoin can help manage more severe rosacea.
Lifestyle Modifications and Triggers to Avoid
Avoiding sun exposure, spicy foods, and hot beverages can prevent rosacea flare-ups.
Natural Remedies for Eczema and Rosacea
For those seeking alternative options, natural remedies can offer relief:
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: Anti-inflammatory foods, such as leafy greens and fish, can reduce skin irritation.
- Gentle Skincare: Mild, fragrance-free products can help soothe sensitive skin.
Preventive Measures for Eczema and Rosacea
Taking proactive steps can help manage both eczema and rosacea:
Skin Care Practices
Moisturize daily, avoid harsh chemicals, and use sunscreen to protect skin.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Stay hydrated, avoid known dietary triggers, and manage stress.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with eczema and rosacea can take an emotional toll. Support groups, counseling, and practicing self-compassion are vital for those navigating these skin conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding eczema and rosacea is the first step toward effective management. With the right diagnosis, treatments, and lifestyle adjustments, those affected can significantly reduce symptoms and enjoy clearer, healthier skin. Remember, if you suspect you have eczema or rosacea, consult a dermatologist for a personalized treatment plan.
FAQs
What is the main difference between eczema and rosacea?
The main difference is that eczema can affect various parts of the body with dry, itchy patches, while rosacea primarily affects the face, causing redness and visible blood vessels.
Can eczema and rosacea be cured?
There’s no cure for either, but both can be managed effectively with the right treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
Are there any foods to avoid with eczema or rosacea?
Yes, certain foods can trigger flare-ups, such as spicy foods for rosacea and dairy or gluten for some with eczema.
How do I know if I have eczema or rosacea?
Consult a dermatologist. They can perform examinations and tests to determine if you have eczema, rosacea, or another condition.
What skincare products are best for sensitive skin with eczema or rosacea?
Opt for gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers, cleansers, and sunscreens designed for sensitive skin.
Click here to read more.