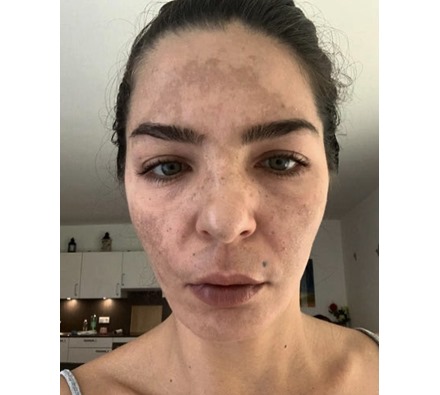
Melasma, a skin condition known for causing dark, brownish patches on the face, can be a challenging issue to address. For residents seeking effective melasma treatment in Loughton, various options are available to help reduce the appearance of these pigmentation spots. While melasma is not harmful, it can affect self-esteem, especially when it appears on visible areas such as the forehead, cheeks, and upper lip. This guide explores the causes of melasma and outlines the best treatments available in Loughton to manage and minimize its impact.
Understanding Melasma
Melasma appears as symmetrical, dark patches on the skin, typically on the forehead, cheeks, nose, and upper lip. It’s often referred to as “the mask of pregnancy” because hormonal changes during pregnancy can trigger it. Melasma can also appear on other parts of the body, especially those frequently exposed to sunlight.
The condition is caused by an increase in melanin, the natural pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. While melanin production is essential, an excess can lead to pigmentation issues like melasma.
Key Factors Contributing to Melasma
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy or while taking hormonal contraceptives, are a significant trigger for melasma.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun stimulates melanin production, making melasma darker and more challenging to treat.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Skin Sensitivity: Certain skincare products, treatments, or cosmetics can irritate the skin, causing or worsening melasma in sensitive individuals.
Types of Melasma
There are three primary types of melasma, categorized based on how deeply the pigmentation affects the skin layers:
- Epidermal Melasma: The pigmentation is located in the upper layer of the skin (epidermis), making it easier to treat. It often appears as a brownish color with well-defined edges.
- Dermal Melasma: This type penetrates deeper into the skin layers and has a bluish-gray appearance. Dermal melasma is more challenging to treat than epidermal melasma.
- Mixed Melasma: A combination of epidermal and dermal pigmentation, mixed melasma presents with both brown and gray patches. Treatment can improve this type, though it may take time.
Understanding the type of melasma you have can help in choosing the right treatment method, and a skincare professional in Loughton can diagnose your type accurately.
Melasma Treatment Options in Loughton
Loughton offers a variety of effective melasma treatment options that range from medical-grade skincare to advanced dermatological procedures. Here’s an overview of some of the best approaches to treating melasma.
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are usually the first line of defense against melasma. Some popular options include:
- Hydroquinone: Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent that reduces melanin production, helping to fade melasma patches. It is available in different strengths, and stronger versions may require a prescription.
- Retinoids: Retinoids, such as tretinoin, increase cell turnover, which can help lighten melasma over time. Retinoids should be used with caution, as they can increase skin sensitivity, especially to sunlight.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant known for its skin-brightening properties, vitamin C reduces the appearance of melasma and protects the skin from further UV damage.
- Azelaic Acid: A gentle alternative to hydroquinone, azelaic acid is effective at reducing melanin production without causing as much irritation, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from mushrooms, kojic acid is a natural brightening agent that can help fade dark spots and reduce pigmentation.
Topical treatments generally require consistent, long-term use to see results. Consulting a dermatologist in Loughton is recommended to determine which topical treatment best suits your skin type.
2. Chemical Peels
Chemical peels use acids to exfoliate the skin, removing the outer layer to reveal brighter, more even-toned skin beneath. This treatment can be particularly effective for epidermal melasma. Some commonly used acids in chemical peels include glycolic, lactic, and salicylic acids.
Chemical peels range in strength from superficial to deep:
- Light Peels: Ideal for mild cases of melasma, light peels have minimal downtime and are safe for most skin types.
- Medium Peels: Suitable for more severe melasma, medium peels require more downtime but offer more dramatic results.
- Deep Peels: These are rarely used for melasma due to their intensity and potential risks, but they can be considered in very stubborn cases.
Chemical peels should always be administered by a trained skincare professional to minimize risks and ensure the best results.
3. Microneedling
Microneedling involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries in the skin, which promotes collagen production and skin regeneration. When combined with serums designed for pigmentation, microneedling can be a powerful tool for treating melasma, especially for those who have not responded well to other treatments.
4. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy for melasma targets pigmented areas with precise light, breaking down melanin deposits and gradually lightening the skin. Some common types of lasers for melasma treatment include:
- Q-Switched Laser: Effective for both epidermal and dermal melasma, Q-switched lasers can provide significant improvement with minimal downtime.
- Fractional Lasers: These lasers create micro-injuries in the skin, encouraging healing and collagen production. They are more intense and may not be suitable for darker skin tones due to the risk of further pigmentation.
Laser therapy requires multiple sessions, and results may vary depending on the skin type and type of melasma. It’s essential to consult with a laser specialist to understand the risks and benefits.
5. Intense Pulsed Light (IPL)
Intense Pulsed Light therapy, or IPL, uses broad-spectrum light to target pigmentation and improve skin tone. While it’s not always the first choice for melasma due to the risk of worsening pigmentation in darker skin tones, it can be effective for lighter skin types with epidermal melasma.
6. PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting your own platelet-rich plasma into the skin to promote healing and cell regeneration. While PRP is commonly used for skin rejuvenation, it can also help improve melasma when combined with other treatments like microneedling. PRP is considered safe with minimal side effects, as it uses your own blood.
At-Home Care Tips for Managing Melasma
In addition to professional treatments, there are several at-home care steps you can take to prevent melasma from worsening and support your skin’s healing process:
- Sun Protection: Sun exposure is one of the main triggers for melasma. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30, wear hats, and avoid peak sun hours whenever possible.
- Consistent Skincare Routine: Gentle cleansing, hydration, and the use of pigment-reducing ingredients like niacinamide, licorice extract, or alpha-arbutin can improve melasma over time. Avoid products with harsh chemicals, as these can irritate the skin and worsen pigmentation.
- Avoid Heat Exposure: Excessive heat from saunas, hot showers, or cooking can exacerbate melasma. Try to keep your skin cool, especially on warmer days.
- Healthy Diet: Eating foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and nuts, can support skin health and may help reduce oxidative stress that contributes to melasma.
- Hydration: Proper hydration helps maintain a healthy skin barrier, which can be beneficial for those with melasma-prone skin. Aim to drink plenty of water daily and use a hydrating moisturizer to keep the skin soft and supple.
Prevention and Maintenance
While melasma can be challenging to treat, consistent care and maintenance can make a significant difference in the appearance of the skin. Prevention plays a major role, so avoid known triggers like sun exposure and hormonal imbalances whenever possible. Establishing a skincare routine that addresses pigmentation and promotes an even skin tone can also help manage melasma over the long term.
Conclusion
Melasma is a complex skin condition that requires a tailored treatment approach. From chemical peels and laser therapy to topical treatments and lifestyle changes, there are multiple strategies to help lighten melasma and even out skin tone. In Loughton, residents have access to a wide range of professional treatments, enabling them to choose a solution best suited to their skin type and lifestyle. Consulting a skincare specialist can provide personalized guidance on managing melasma and help you achieve healthier, more radiant skin.