Introduction
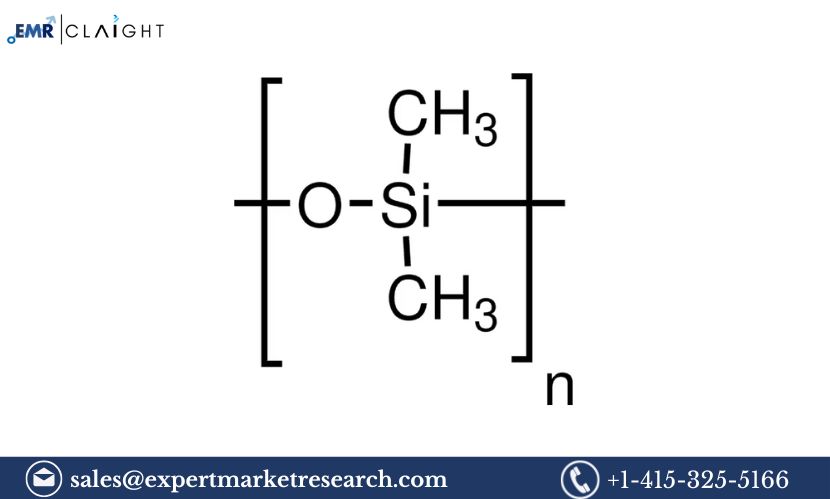
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a type of silicone polymer known for its versatility, excellent thermal stability, water-repellent properties, and non-toxic nature. Widely used in industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and construction, PDMS is used in applications ranging from lubricants and sealants to skin-care products and medical devices. A Polydimethylsiloxane Manufacturing Plant Project Report serves as a detailed guide for establishing a facility that produces PDMS, outlining all critical aspects including market opportunities, production processes, financial planning, safety protocols, and regulatory compliance.
Market Overview
The market for Polydimethylsiloxane is driven by its widespread industrial applications, including in personal care products, automotive coatings, food processing, and medical devices. Its unique properties make it indispensable in multiple sectors, resulting in a steadily growing global demand.
Key Drivers of Market Growth:
- Increasing Demand for Silicone-Based Products: With the growing demand for high-performance materials, PDMS has become a preferred choice in industries like cosmetics, automotive, and healthcare.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in silicone production technology have made PDMS more cost-effective, enabling its use in a broader range of applications, from electronics to medical devices.
- Environmental and Health Benefits: PDMS is considered safe for human health and environmentally friendly compared to traditional chemicals, driving its adoption in consumer products and medical devices.
- Expanding Automotive and Construction Sectors: PDMS is increasingly used in automotive applications such as lubricants, coatings, and electrical components, and its use in construction materials like sealants is also rising.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Challenges:
- High Production Costs: The production of PDMS requires specialized equipment and raw materials, which can lead to relatively high manufacturing costs.
- Supply Chain Constraints: The sourcing of key ingredients, such as silica, and ensuring consistent quality can be a challenge for manufacturers.
- Environmental Concerns: Despite its advantages, the manufacturing process of PDMS can sometimes involve energy-intensive procedures, which may lead to concerns about sustainability and waste management.
Project Overview
The Polydimethylsiloxane Manufacturing Plant Project Report outlines the steps necessary to establish a successful PDMS manufacturing plant, from feasibility studies and market research to financial planning, production processes, and safety measures.
Feasibility Study
Before beginning production, a thorough feasibility study is essential to evaluate market potential, assess financial viability, and identify risks. This includes:
1. Market Demand Analysis:
End-User Industries: The primary markets for PDMS include the automotive, construction, healthcare, and cosmetics industries. An analysis of the demand for PDMS in these sectors can provide insights into production capacity needs.
Geographical Market Trends: PDMS consumption varies by region, with significant demand in developed markets such as North America and Europe, as well as emerging markets in Asia-Pacific.
2. Raw Material Sourcing:
The key raw materials for PDMS production include silica, methyl chloride, and silicon. Establishing reliable and cost-effective supply chains for these materials is crucial for the plant’s success.
3. Technology and Equipment:
The production of PDMS requires specialized reactors, filtration systems, and drying equipment. Investment in high-quality, energy-efficient equipment can help reduce production costs and improve product quality.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
The manufacturing of PDMS falls under regulatory frameworks related to chemical production and consumer safety. Compliance with environmental and safety regulations is essential.
Site Selection and Infrastructure
When selecting a location for the PDMS manufacturing plant, several factors must be considered:
- Proximity to Raw Material Sources: The plant should be located near suppliers of silica and other chemicals to reduce transportation costs and ensure steady material supply.
- Access to Infrastructure: A location with good access to transportation (e.g., highways, ports) will make distribution easier and more cost-effective. Additionally, proximity to energy sources will support the energy-intensive nature of PDMS production.
- Environmental Impact: The location should be chosen with consideration for environmental regulations. PDMS manufacturing can generate waste byproducts, and having a waste disposal plan is crucial.
Production Process
The production of Polydimethylsiloxane involves a series of steps, from the preparation of raw materials to the final packaging of the product.
1. Raw Material Preparation:
Silica Activation: Silica, a key raw material, is first activated in the presence of methyl chloride and a catalyst to initiate the reaction.
Polymerization: The activated silica undergoes polymerization in a controlled reactor, where methyl groups are added to form the silicone polymer chains.
2. Polymerization and Reaction:
Reaction Conditions: The polymerization process requires specific conditions such as temperature, pressure, and catalyst concentration. These parameters are adjusted to achieve the desired viscosity and molecular weight of the PDMS.
3. Filtration and Purification:
After polymerization, the PDMS undergoes filtration and purification to remove any unreacted chemicals or impurities.
4. Drying and Packaging:
The final product is dried to eliminate any residual solvents and moisture before being packaged in appropriate containers for shipment. Packaging may vary depending on the intended application (e.g., bulk for industrial use or small units for consumer products).
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Given the chemical nature of PDMS production, safety is paramount. Key safety measures include:
- Protective Equipment: Workers involved in the production process should wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
- Ventilation and Containment: The plant should be equipped with proper ventilation systems to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes and gases. Reactors should also have containment systems to prevent leaks or spills.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal of chemical waste, including byproducts of the polymerization process, is crucial to reduce environmental impact. Recycling and reusing waste where possible can contribute to sustainability.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient equipment and processes can help reduce the carbon footprint of the plant and lower operational costs.
Financial Planning
The financial aspect of establishing a PDMS manufacturing plant involves several considerations:
- Capital Investment:
- Establishing the plant requires significant capital for land, building construction, machinery, and raw materials. Additionally, investments in R&D for product development may be needed.
- Operational Costs:
- Ongoing costs will include raw material purchases, labor, energy consumption, and maintenance of equipment. Effective cost management will be essential for profitability.
- Revenue Projections:
- Revenue generation will depend on factors such as product pricing, demand from end-use industries, and production capacity. A well-defined pricing strategy should be developed based on market analysis.
- Return on Investment (ROI):
- ROI calculations will assess the potential profitability of the venture by comparing projected revenues to capital investment and operating costs.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
A robust marketing strategy is vital for gaining market share in the competitive PDMS industry:
- Target Markets:
- PDMS can be marketed to a variety of industries, including automotive (lubricants and coatings), healthcare (medical devices), personal care (cosmetics), and construction (sealants).
- Brand Positioning:
- Position PDMS as a high-quality, versatile, and environmentally-friendly product suitable for various industrial applications. Emphasize its long lifespan and safety.
- Distribution Channels:
- Distribute the product through industrial distributors, wholesalers, and direct sales to large companies. Partnerships with key industries can help expand reach.
- Promotions and Partnerships:
- Attend industry conferences, advertise in trade journals, and engage in digital marketing to raise awareness. Form strategic partnerships with industries that use PDMS extensively.
FAQs
1. What is Polydimethylsiloxane used for?
Polydimethylsiloxane is used in a variety of industries, including automotive, healthcare, cosmetics, and construction, due to its excellent thermal stability and non-toxic properties.
2. How is Polydimethylsiloxane manufactured?
PDMS is produced through the polymerization of silica and methyl chloride under controlled conditions, followed by purification and packaging.
3. Is Polydimethylsiloxane safe for use in consumer products?
Yes, PDMS is non-toxic and is commonly used in personal care products, such as shampoos, lotions, and cosmetics, as well as medical devices.
4. What are the environmental concerns of PDMS production?
The production of PDMS can generate waste byproducts and consume significant energy, which requires proper waste management and energy-efficient processes.
5. What industries use Polydimethylsiloxane?
Industries such as automotive (for lubricants and coatings), healthcare (for medical devices), cosmetics (for skin care products), and construction (for sealants) extensively use PDMS.
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au